Node to Node Communication
dbWatch Control Center operates in a distributed architecture, composed of multiple interconnected nodes—including Control Center servers, monitors, routers, and instance hubs. These nodes communicate using a multi-layered protocol designed for security, routing flexibility, and encrypted messaging.
This page explains how node-to-node communication works internally, including how authentication, TLS, and ephemeral encryption are used to securely transmit messages.
This section assumes familiarity with node roles. See Core Concepts & Architecture if you’re new to the terminology.
Layered Protocol Stack
The dbWatch protocol consists of the following layered components:
- TCP/IP: Base transport layer for connectivity between nodes
- TLS: Encrypted channel with certificate-based mutual authentication
- Message Layer: Signed and optionally encrypted messages routed between nodes
- Ephemeral Tunnel: Additional end-to-end encryption of message bodies using Diffie-Hellman key exchange
The dbWatch Monitor is considered a node and follows the same communication principles.
1. TCP/IP Layer – Node Connectivity
Nodes connect using standard TCP sockets. Each node may:
- Accept incoming connections on one or more ports (e.g., 7100/tcp)
- Initiate outbound connections to peer nodes
Configuration options are available in:
Configuring node connections can be done in the Domain Configuration, by right clicking on a node and selecting Edit connections
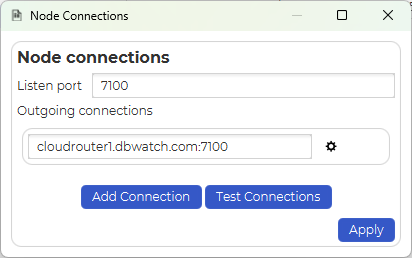
The underlying config file is “[dbWatch Work]/config/node/node.connections”
Example of a “node.connections” file:
{
"versionCutoff":"",
"nodeCost":"0",
"listenTo":[
"dbw://localhost:7100"
]
, "connectTo":[
"dbw://cloudrouter1.dbwatch.com:7100"
]
}See also:
Network and Communication Setup
2. TLS Layer – Secure Transport with Routing Privileges
All TCP communication is wrapped inside a TLS channel, offering:
- Encryption in transit (AES/GCM)
- Mutual certificate-based authentication
- Domain-based routing authorization
Each node presents its domain-issued certificate. During TLS negotiation:
- Nodes present proof of routing privileges (based on domain)
- A node will only forward traffic between peers that share at least one trusted domain
This ensures zero-trust communication across a multi-node topology.
Learn more about the certificate system here:
Certificate Infrastructure
3. Message Layer – Routed Message Encapsulation
Each dbWatch message includes routing metadata and a cryptographic signature. The message is forwarded across multiple nodes, if necessary, until it reaches its final destination.
| Field | Description | Size (bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| time to live | Hop count / TTL to avoid loops | 1 |
| recipient | IPv6-style recipient address | 16 |
| sender | IPv6-style sender address | 16 |
| body category | Type of message payload | 1 |
| send time | Epoch timestamp | 8 |
| certificate ID | ID of signing certificate | 8 |
| is body encrypted | Indicates whether payload is encrypted | 1 |
| body length | Length of message body | 4 |
| message body | Encrypted or plaintext content | variable |
| signature length | Length of digital signature | 4 |
| signature | Signature of all above fields (except TTL) | variable |
- Messages addressed to the local node are validated and decrypted before processing.
- Messages in transit are routed based on recipient address.
- Signatures ensure the authenticity and integrity of all messages.
4. Ephemeral Tunnel – End-to-End Message Encryption
Since TLS only encrypts between directly connected nodes, dbWatch uses a second encryption layer for message confidentiality:
- Each pair of nodes performs an Elliptic-Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) handshake
- The derived ephemeral session key is used to encrypt the message body before it enters the network
- This ensures end-to-end secrecy, even if an intermediate router node is compromised
- It also provides forward secrecy: compromising a server’s certificate later will not reveal historical traffic
This layered encryption approach protects against:
- Packet sniffing
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
- Message tampering or spoofing
Learn more:
Encryption and Ephemeral Keys
Key Advantages
- Secure multi-hop routing of messages between nodes
- Authentication and domain-aware routing via certificates
- TLS protection combined with forward-secret message encryption
- Configurable listening and connection topologies
- Supports air-gapped, segmented, or cloud-native deployments
Related Topics
If you require assistance with multi-node topologies, secure routing, or troubleshooting connection paths, contact:
support@dbwatch.com