Adding a SQLServer instance
How to get here
To open the “Add Instance Wizard”, click on the “Plus (+)” sign on the bottom left of the dbWatch Client.
Select Instance Type and Input Connection Details
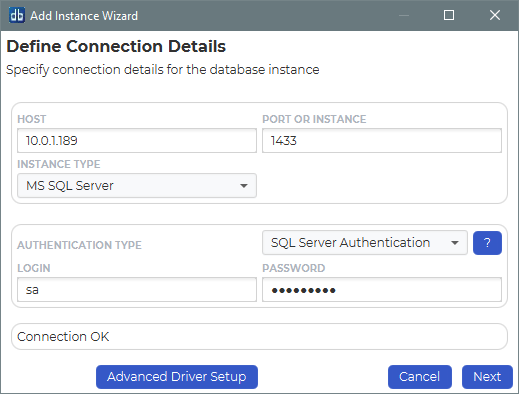
Specify the host and port number.
dbWatch will attempt to select the correct instance type based on the entered port number. If the instance type is wrong, select the correct one in the drop down.
The authentication types available will depend on the selected instance type.
Choose an authentication type whether “SQL Server Authentication”, “OS Authentication” or “Kerberos”.
You need to specify a login with a server administrator role that will be used during the installation.
| OS Authentication | Connects to the MS SQL Server using the account the dbWatch Server Services is running under. This could require additional configuration, more here |
| SQL Server Authentication | Connects using the provided login and password. |
| Kerberos | Connects through kerberos using the provided login and password. This could require additional configuration, more here |
By default dbWatch will select the most appropriate JDBC driver for the database instance. It is possible to select a specific JDBC driver and set driver properties by clicking on Advanced Driver Setup.
Click “Next”.
TLS Compatibility for Older Microsoft SQL Server Versions
Secure TLS communication is required between the dbWatch Control Center and Microsoft SQL Server instances.
Some older SQL Server versions (typically SQL Server 2014 and earlier, and unpatched SQL Server 2016 installations) only support TLSv1 by default.
Recent Java versions used by dbWatch Control Center disable TLSv1 unless explicitly enabled, which may prevent successful connections to these database versions.
If you are monitoring such SQL Server versions, TLSv1 support can be enabled in dbWatch Control Center by updating the Java security configuration.
See:
MS SQL Server TLS requirements
Important:
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 is not supported by dbWatch Control Center.
Connection attempts to SQL Server 2005 have not been successful in practice, even when enabling TLSv1 as described above.
Define Monitoring
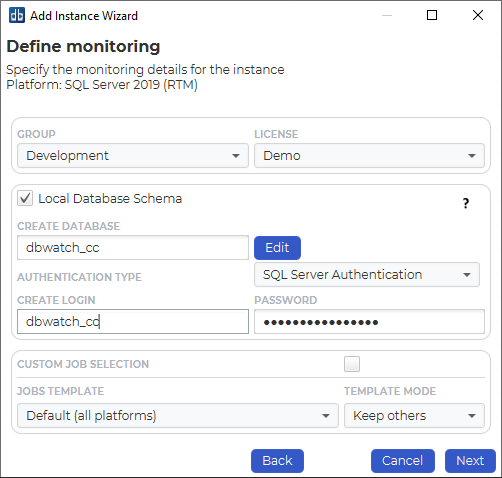
Specify the group and license for the instance. Default groups are Development, Test and Production, but you can easily create and customize your own groups based on your requirements.
The licensing options available will depend on your license. The selected option will determine what monitoring jobs are available.
You can choose to register this instance with or without a local database schema. This choice will influence the available monitoring jobs. Some jobs require objects in the database (procedures, tables etc.), others do not. We recommend installing a database schema, as this will give the most monitoring options.
By default you install the jobs that are part of a template. You can choose the template you use, and have your own custom templates. If you want to enable custom job selection while adding the instance, you can click on the “Custom job selection” radio button.
Click “Next”.
If you do that the next window will allow this selection:
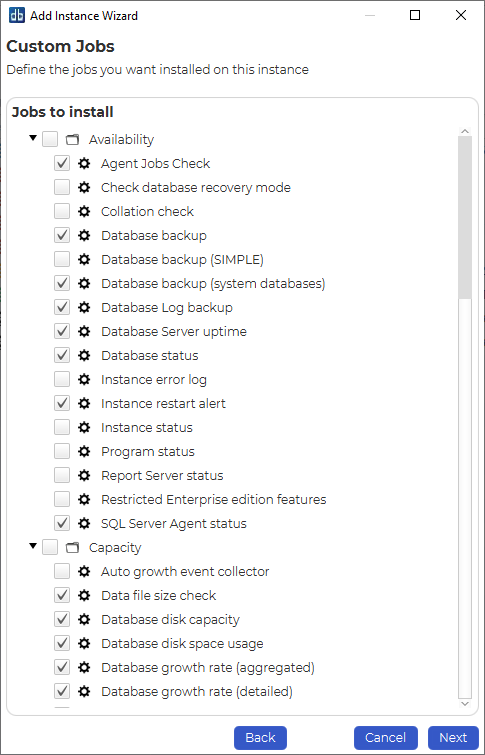
You can stick with the jobs that are selected by default or customize the selection as needed.
Click “Next”.
Define Module authentications
Within this window you have an option to choose which credential to use for each module within dbWatch.
You can use the existing credentials, or select specify a new one.
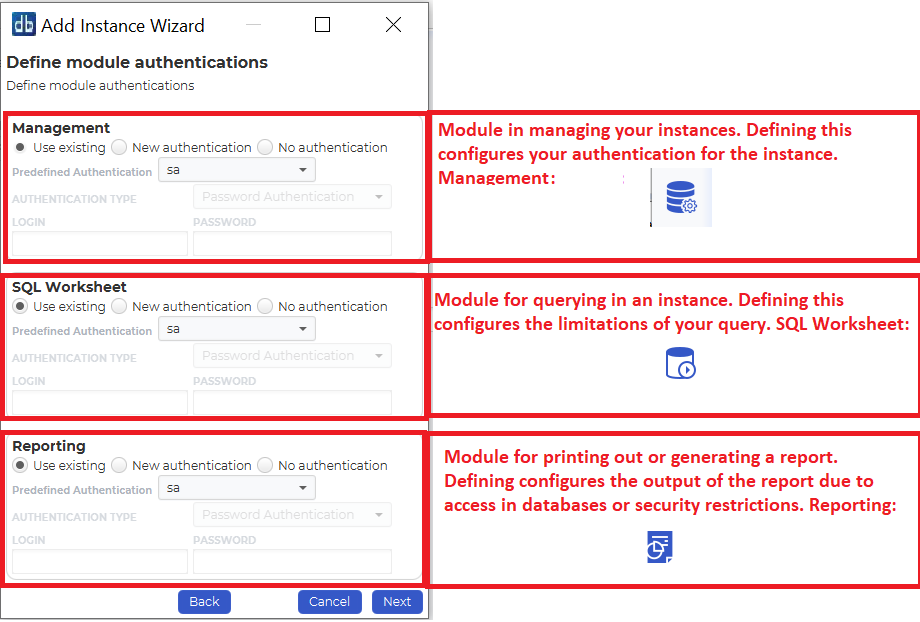
If you’ve finished specifying a credential for each module. Click Next.
Instance Installation
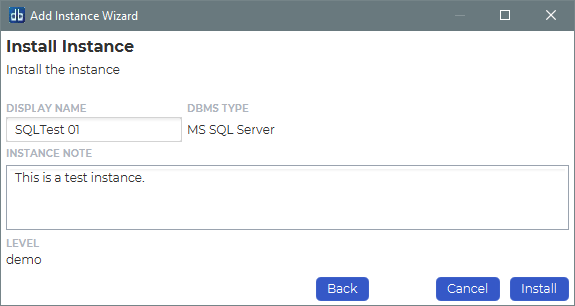
Specify a display name for this instance. You can also provide a description or any relevant information you want to remember about this instance.
Click Install to start installing.
Underneath you will see the status of various jobs being installed.
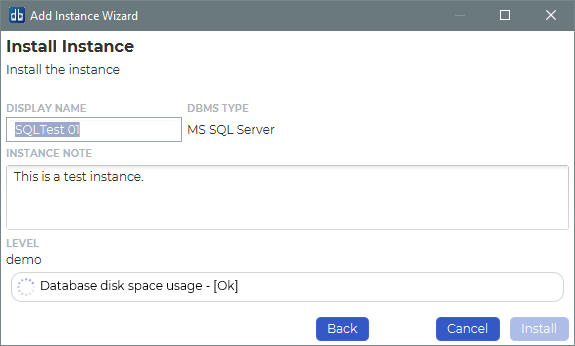
We’ve now successfully added the SQL Server instance in our dbWatch monitor.