SQL Worksheet
One of the truly unique features of dbWatch is its integrated SQL Worksheet, which, although easy to use has sophisticated applications, including cross-database queries.
The SQL Worksheet is meant to give responsible DBA’s the ability to locate any problems and correct them, without having to switch between a multitude of tools (same SQL Worksheet for all supported databases).
It is not developed from a developer-centric perspective and therefore doesn’t include many developer-oriented features such as code optimization or analysis features.
The toolbar along the top of the SQL Worksheet allows you to load and save SQL queries from file and save the output to file.
The tree on the lower left side lets you select among all the instances that are available in Control Center. On the right side of the window shows the query tab for you to write your queries.
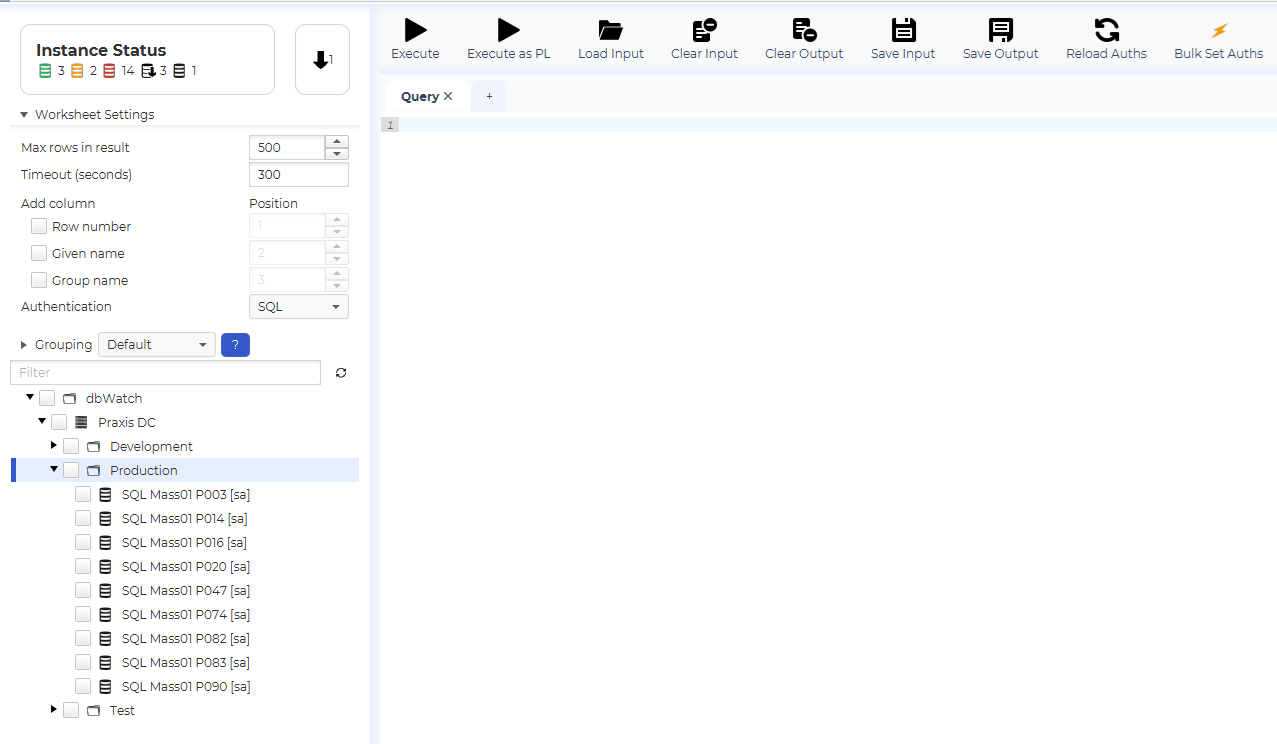
First let us select an instance, for example the “SQL Mass01 P003” instance. In the example we have typed a query that returns the number of active sessions on the instance. Execute the query by clicking on the “Execute” button, or by hitting “Ctrl+E”.
Notice that the current login is shown in the square brackets after the instance name in the tree.
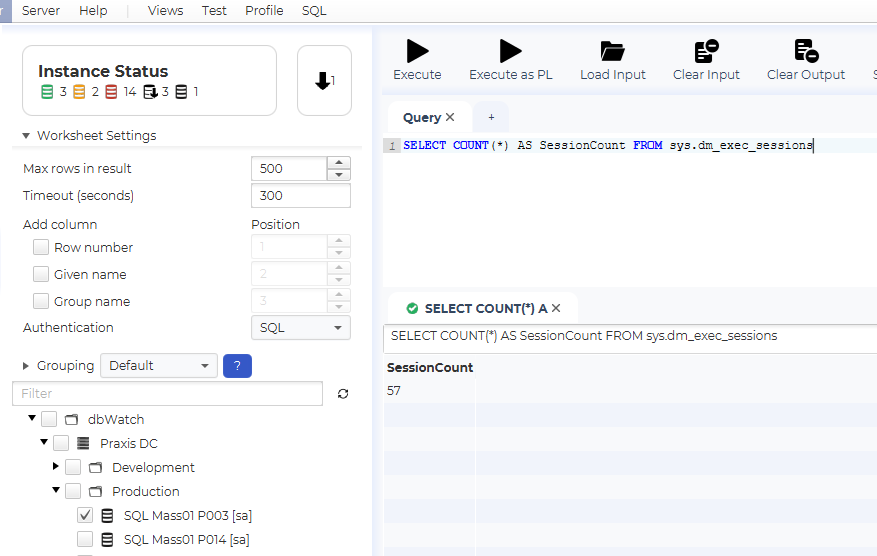
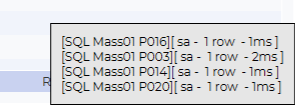
As you can see, we get a single row with the excpected result.
Now let’s try one of the cool features of the SQL Worksheet. Select additional instances in the instance tree, and hit Execute.
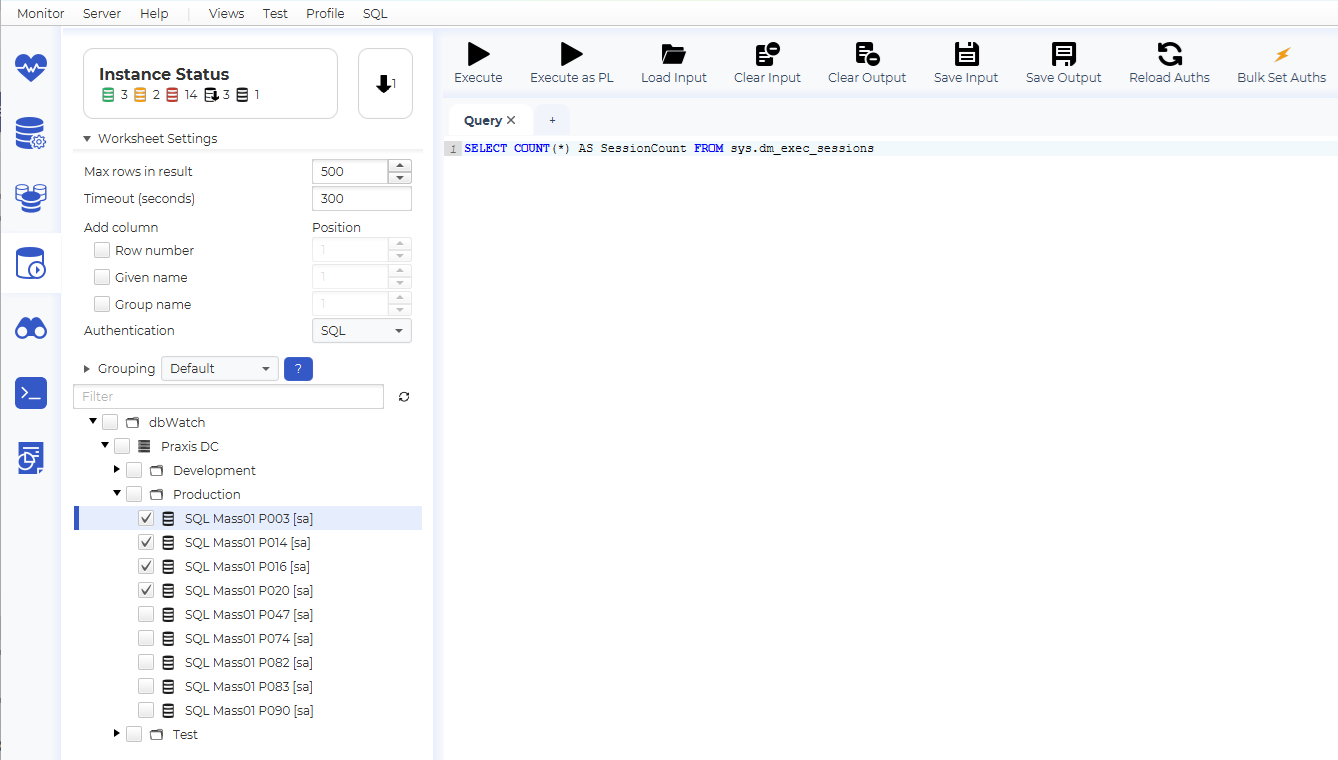
As you can see, we get one row for each selected instance. This is nice, but we can not tell what instance each result row belongs to.
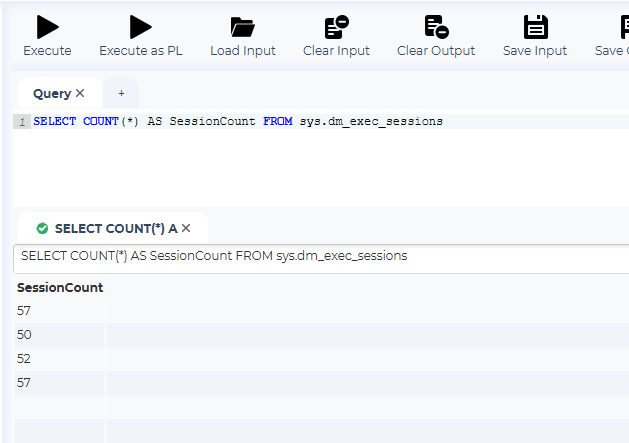
To remedy this, select the “Given name” checkbox in the “Worksheet Settings” section, and execute the query again.
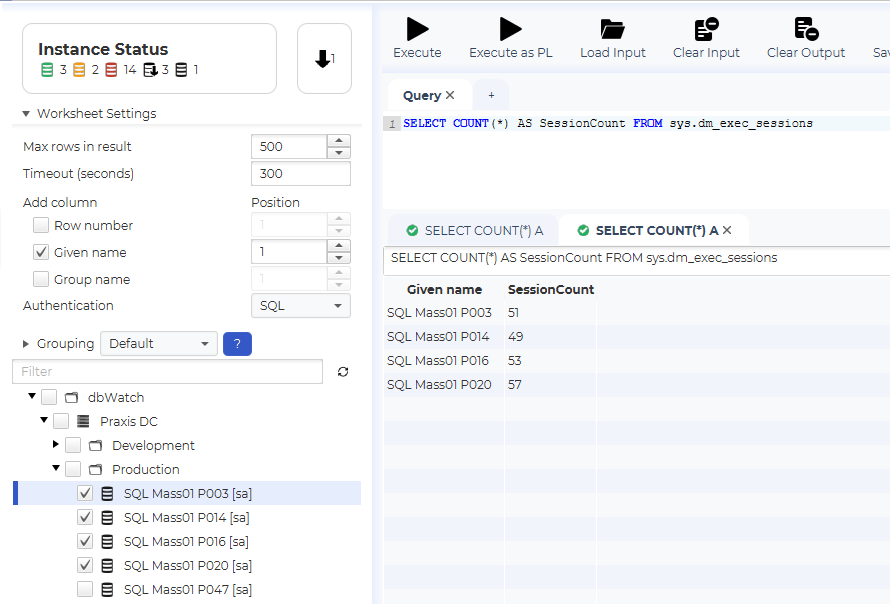
As you can see, we now get an additional column with the name of each instance. It is also possible to add a row number and the group name for each instance.
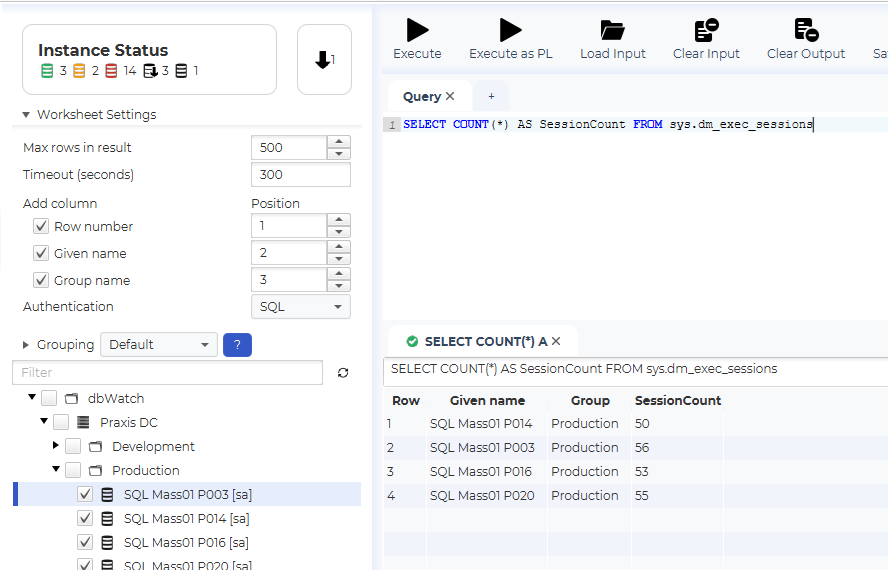
The example only returns one row per instance, but there are no limits on what types of results you can merge in this way. The only requirement is that all instances must return the same number of columns.
If the selected instances are registered to different dbWatch Servers, you will get one result tab per dbWatch Server.
Go ahead and play around with it yourself to see more of this amazing feature.
Execution details
In the lower right corner, you can see additional details about the last execution.
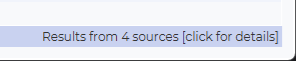
If we click on it, we see a summary telling us what user we are connected as, how many rows was returned and the execution time.
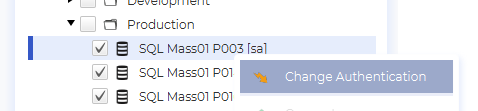
Change authentication
You can access the “Configure Authentication” dialog for an instance by right clicking the instance and clicking “change authentication.”
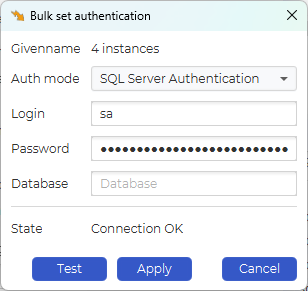
After that, input the login credentials. For database platforms where it is relevant, you can opt to specify a specific database or leave empty to use the default.

It is also possible to set the authentication of multiple database instances in bulk. Select the instances you want to set the authentication for and click “Bulk Set Auths” on the toolbar.
The “Test” button will test the provided authentication on the first selected instance.
Result formating
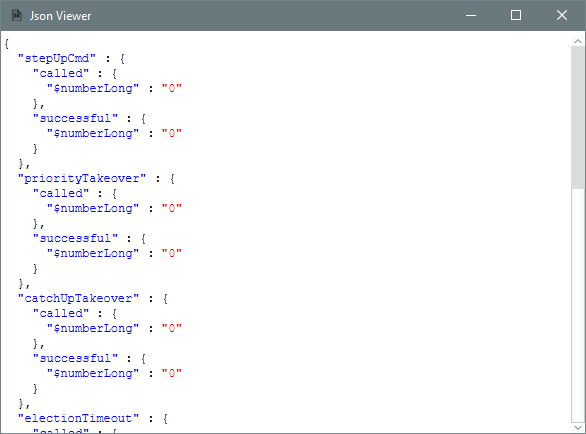
Some databases return results in JSON format. When this is the case it is possible to right click on a cell and select “View as JSON“.
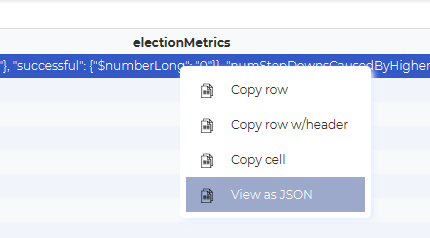
This will open a view with the cell content formatted as JSON.