Using SQL Performance package on MySQL
Navigating to the SQL Performance package dashboard
Once the SQL statistics job is installed and have collected data, you can navigate to the dashboard.
It is located in the management interface for that database instance. The pictures and descriptions are from MySQL.
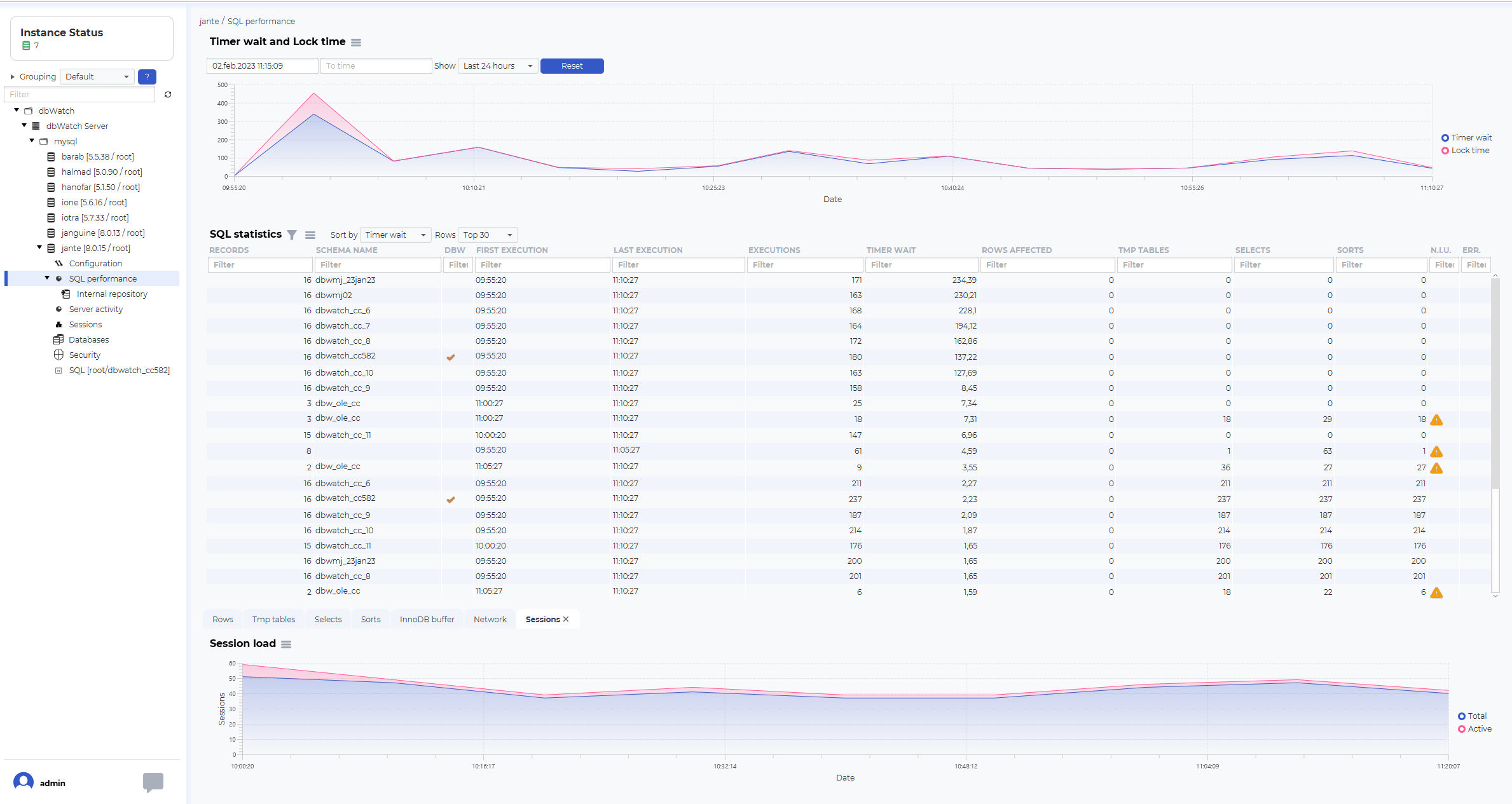
There should be a “SQL performance” node in the three structure. Click on it to open the SQL Performance dashboard.
Using the SQL Performance dashboard
Navigating time
The structure of the SQL Performance dashboard is a top graph showing historical data, such as timer wait and lock time.
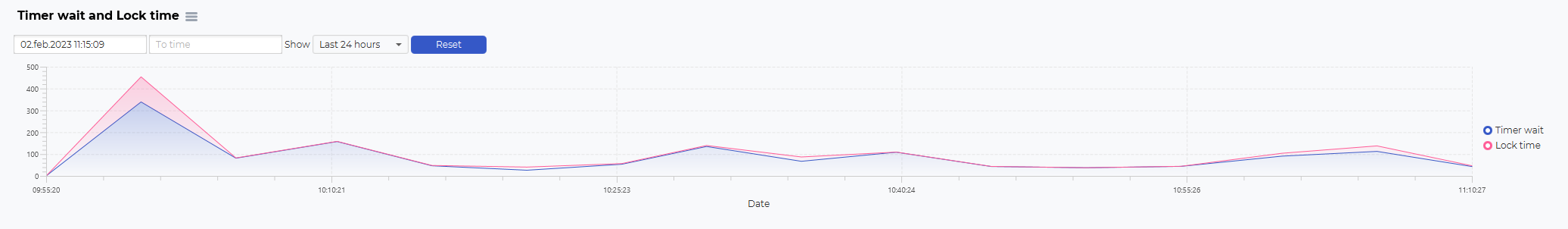
The blocks graph is used to select the timeframe you want to look at.
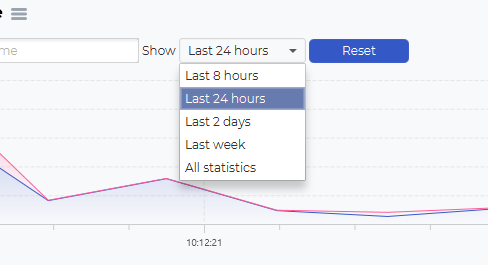
You can select predefined time selections, such as Last 8 houres, Last 24 houres, Last 2 days, Last week and all statistics:
You can also use the mouse to select a timeframe from the graph. Click on your start time, hold the mouse button, drag to the desired end time, and release the mouse button.
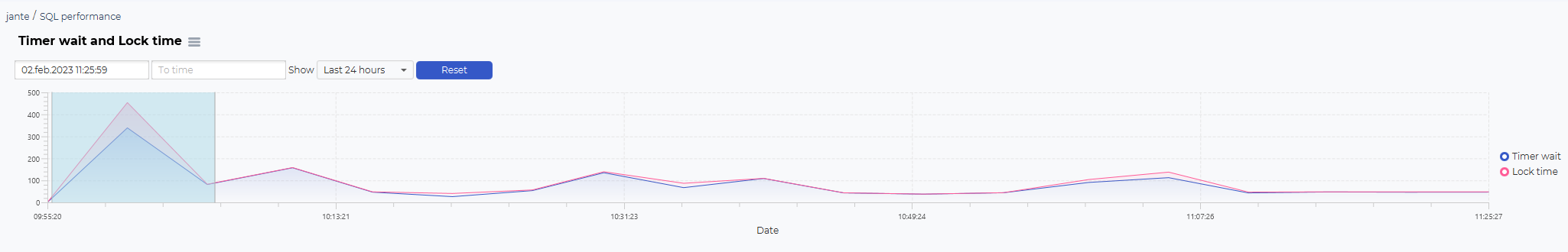
This will change the selection on the SQL statistics table and the additional information graphs.
SQL statistics
The SQL statistics will list SQL statements that has been active in the selected time period.
The fields
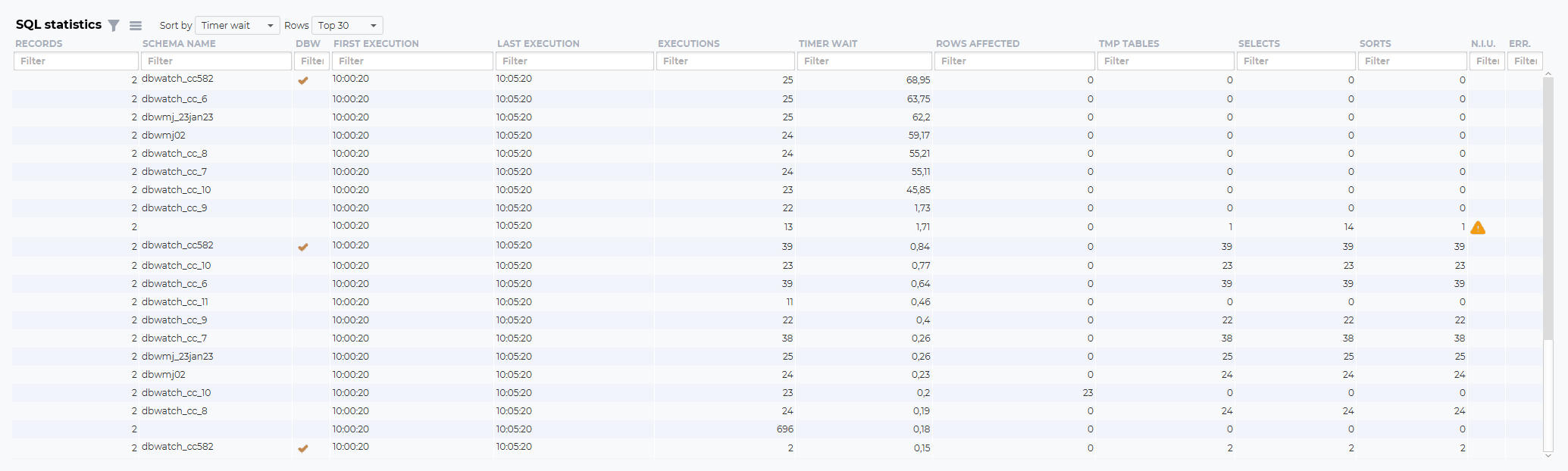
Records:
The number of times this SQL statements has been detected by dbWatch
Schema name:
The schema name executing the SQL or procedure
DBW:
Is this a SQL or procedure associated with dbWatch
First execution:
The first time in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
Last execution:
The last time in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
Executions:
The number of times in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
Timer wait:
The total wait time (in milliseconds) in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
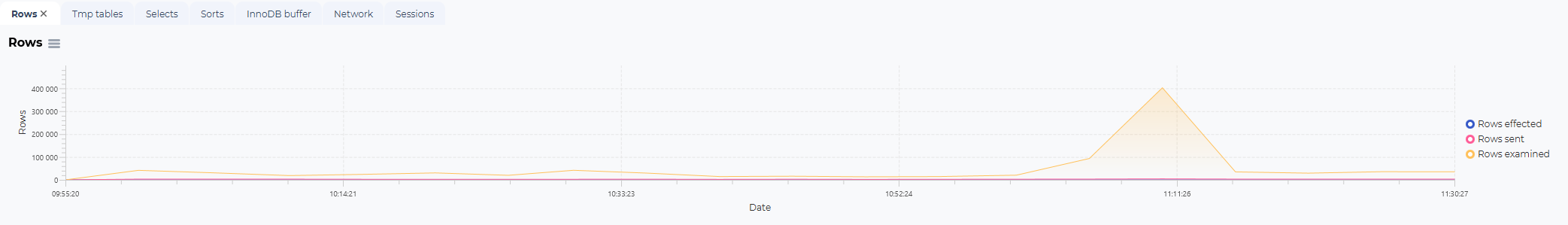
Rows affected:
The total number of rows affected*in the selected time frame* where this SQL or procedure was executed
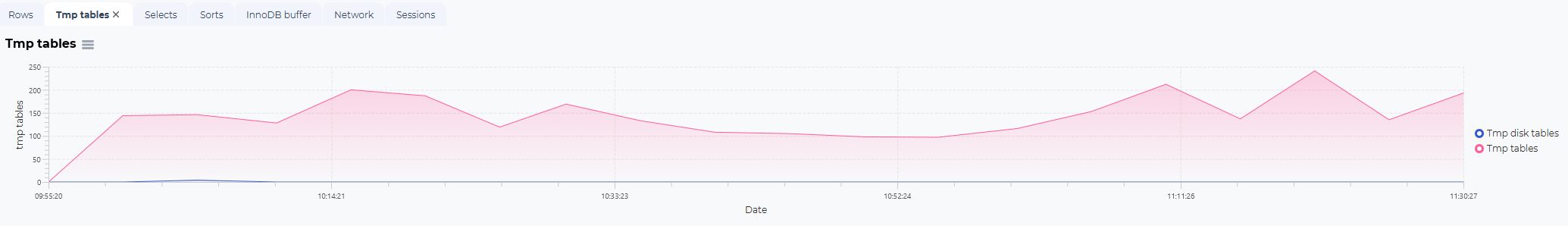
TMP tables:
The number of tmp tables created in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
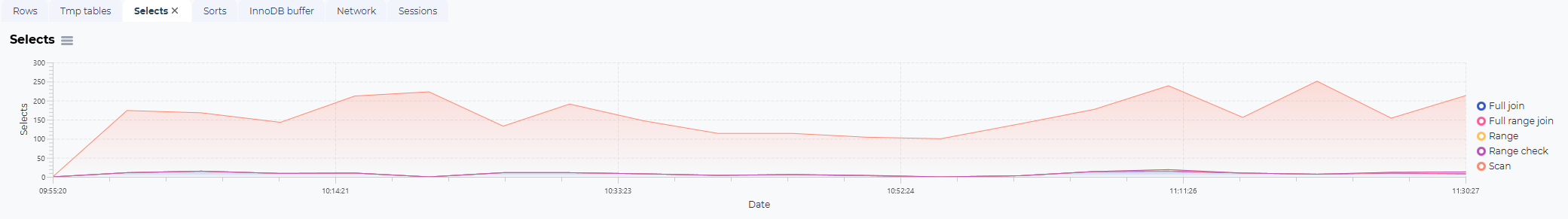
Selects:
The number of selects in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
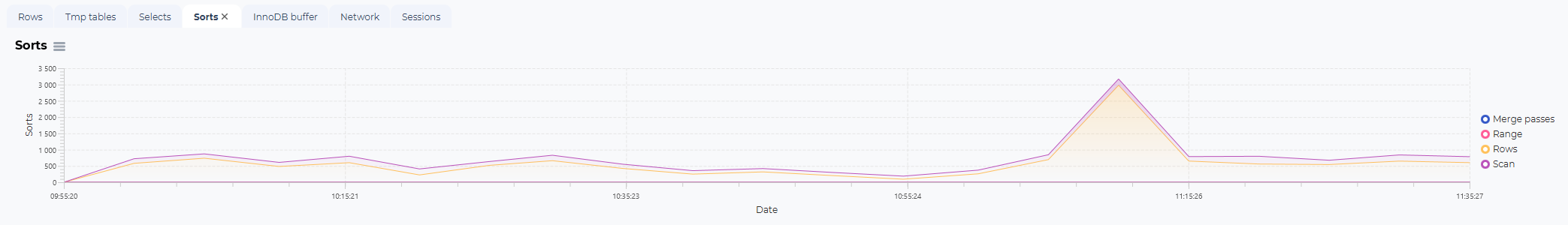
Sorts:
The number of sorts in the selected time frame where this SQL or procedure was executed
N.I.U.:
Indicating Not In Use indexes.
Err.:
Indicating errors with this query.
Navigating SQL statistics
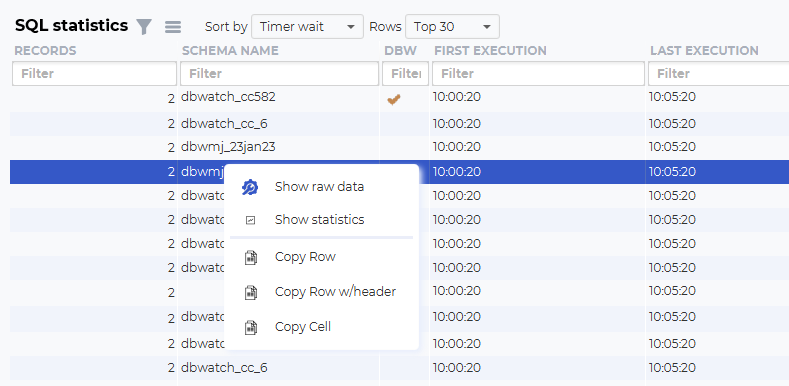
You can investigate the SQL further by right-clicking on one of the lines. Show statistics will open a new dashboard focusing on one SQL statement.
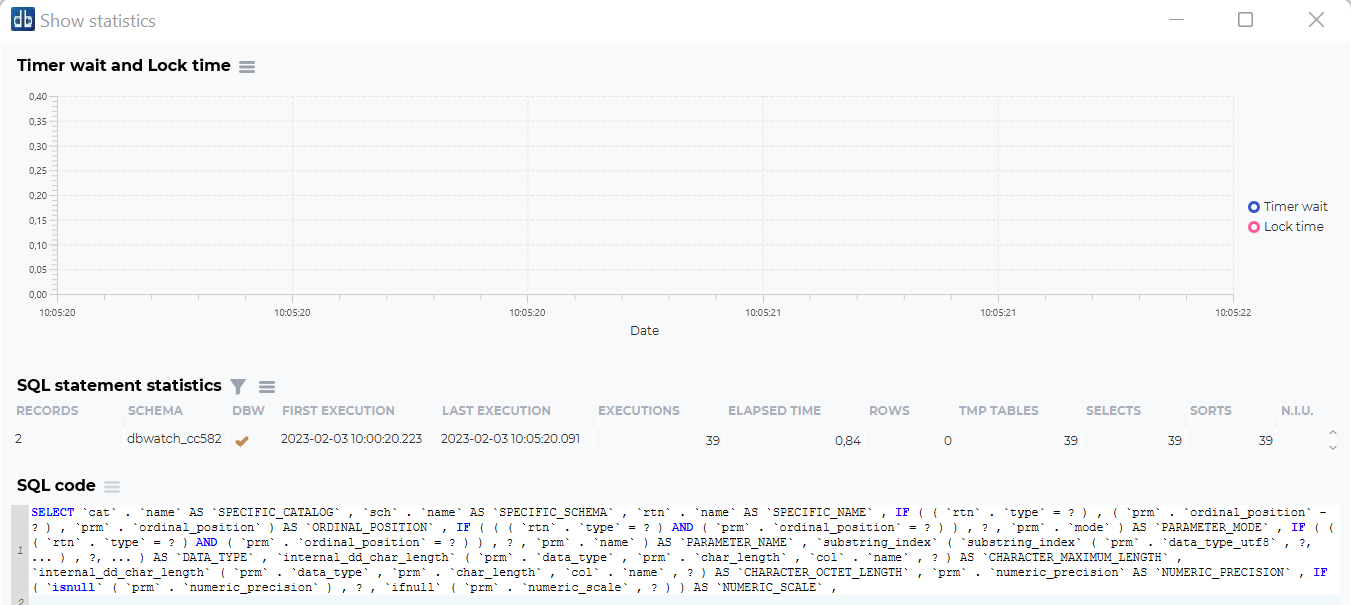
This dashboard will show timer wait and lock time statistics for this statement, and the statistics for the SQL code that has been run.
Additional graphs
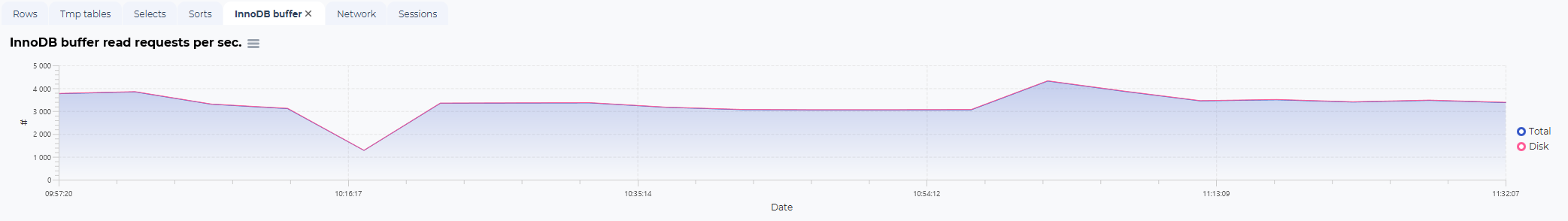
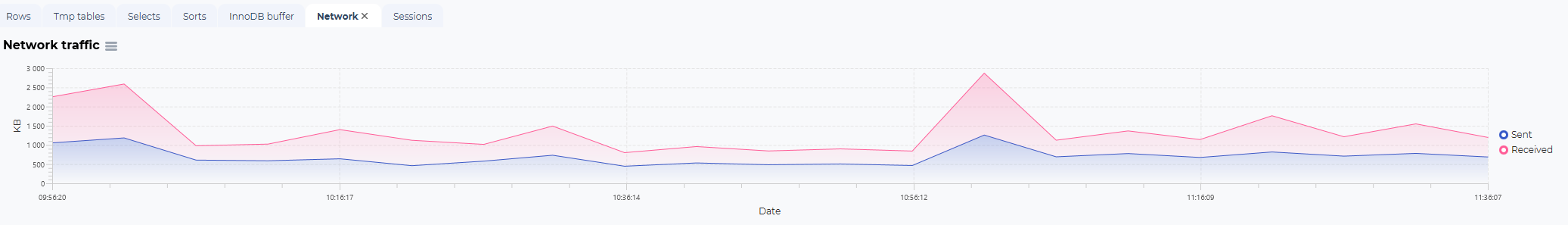
In addition to the logical/physical reads and writes and the SQL statistics overview, there are additional graphs to visualize other performance statistics from the same selected timeframe.
Examples:
Rows statistics:
TMP tables statistics:
Selects statistics:
Sort statistics:
InnoDB buffer statistics:
Network usage statistics:
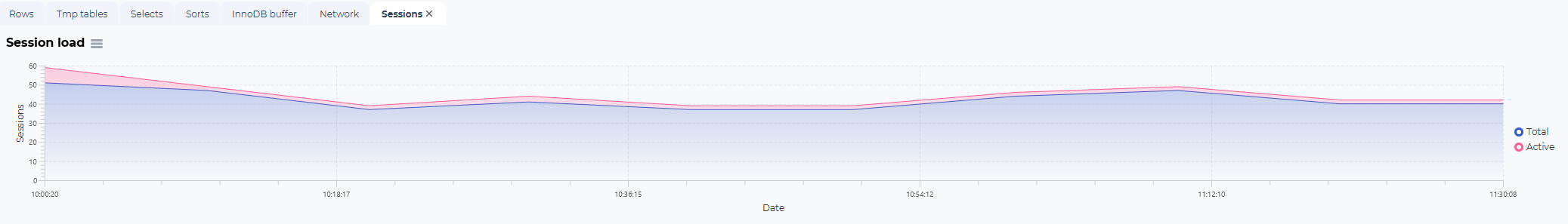
Sessions load: